Pregnancy is one of the most significant milestones in a woman’s life, filled with excitement, anticipation, and sometimes anxiety. One of the best ways to ensure a healthy pregnancy and a smooth delivery is by committing to proper prenatal care. Regular checkups, ultrasounds, and screenings are crucial in ensuring both the mother and the baby are healthy throughout the pregnancy.
In this blog post, we will dive deep into the significance of these essential components of prenatal care, how they help in monitoring your baby’s development, and why they are critical for identifying potential issues early on.
What Is Prenatal Care?
Prenatal care refers to the medical attention that a pregnant woman receives from the time she learns she is pregnant until she gives birth. This care includes routine checkups, tests, ultrasounds, and advice that help monitor the health of both the mother and the baby. It is a proactive way of detecting and managing potential risks during pregnancy.
This form of care not only ensures that the baby is developing well but also equips the mother with the knowledge and support she needs throughout the pregnancy journey.
The Importance of Regular Prenatal Checkups
One of the cornerstones of prenatal care is regular checkups. These checkups are typically scheduled:
- Monthly for the first 28 weeks of pregnancy.
- Bi-weekly from 28 to 36 weeks.
- Weekly from 36 weeks until birth.
These checkups involve a thorough examination and provide valuable insights into both the mother’s and baby’s health. Here’s why regular prenatal checkups are so important:
1. Monitoring Fetal Growth and Development
At each checkup, the healthcare provider will assess the baby’s development to ensure it is progressing as expected. This includes:
- Measuring the size of the uterus to check the baby’s growth.
- Listening to the baby’s heartbeat.
- Monitoring the baby’s movements.
- Checking the mother’s weight gain and overall health.
Regular monitoring of these factors ensures that any irregularities in the baby’s growth are detected early, allowing for prompt intervention if necessary.
2. Detecting and Managing Complications
Pregnancy can sometimes bring unexpected complications such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, or issues with the placenta. Regular checkups allow healthcare providers to detect and manage these complications before they become serious problems.
For example, gestational diabetes can affect both the mother and baby if left untreated, leading to excessive birth weight or premature birth. Early diagnosis through regular testing can help manage this condition with dietary changes and medical support.
3. Ensuring the Mother’s Health
A mother’s health during pregnancy is just as important as the baby’s. Routine prenatal visits often include blood pressure checks, urine tests, and blood tests to monitor for signs of preeclampsia, infections, or anemia.
Preeclampsia, which is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine, can be life-threatening if left untreated. Regular prenatal checkups are essential for monitoring the mother’s blood pressure and ensuring early intervention when needed.
4. Providing Education and Emotional Support
Pregnancy can be an emotional time, filled with questions and concerns. Prenatal visits are an opportunity to ask your healthcare provider about any symptoms, lifestyle changes, or emotional challenges you might be facing. These checkups can help alleviate fears and provide clarity about what to expect in the coming weeks.
Healthcare providers also offer valuable education during these visits, including advice on nutrition, exercise, and how to prepare for childbirth.
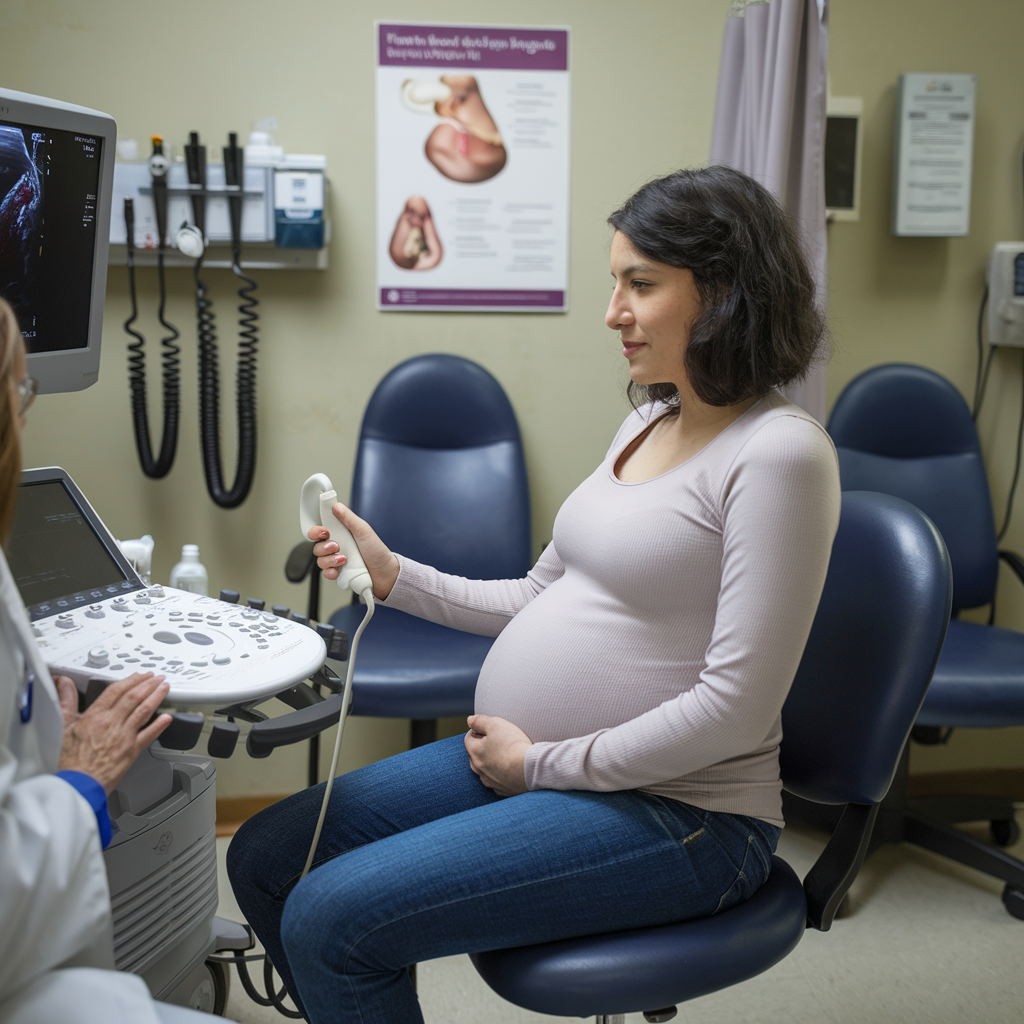
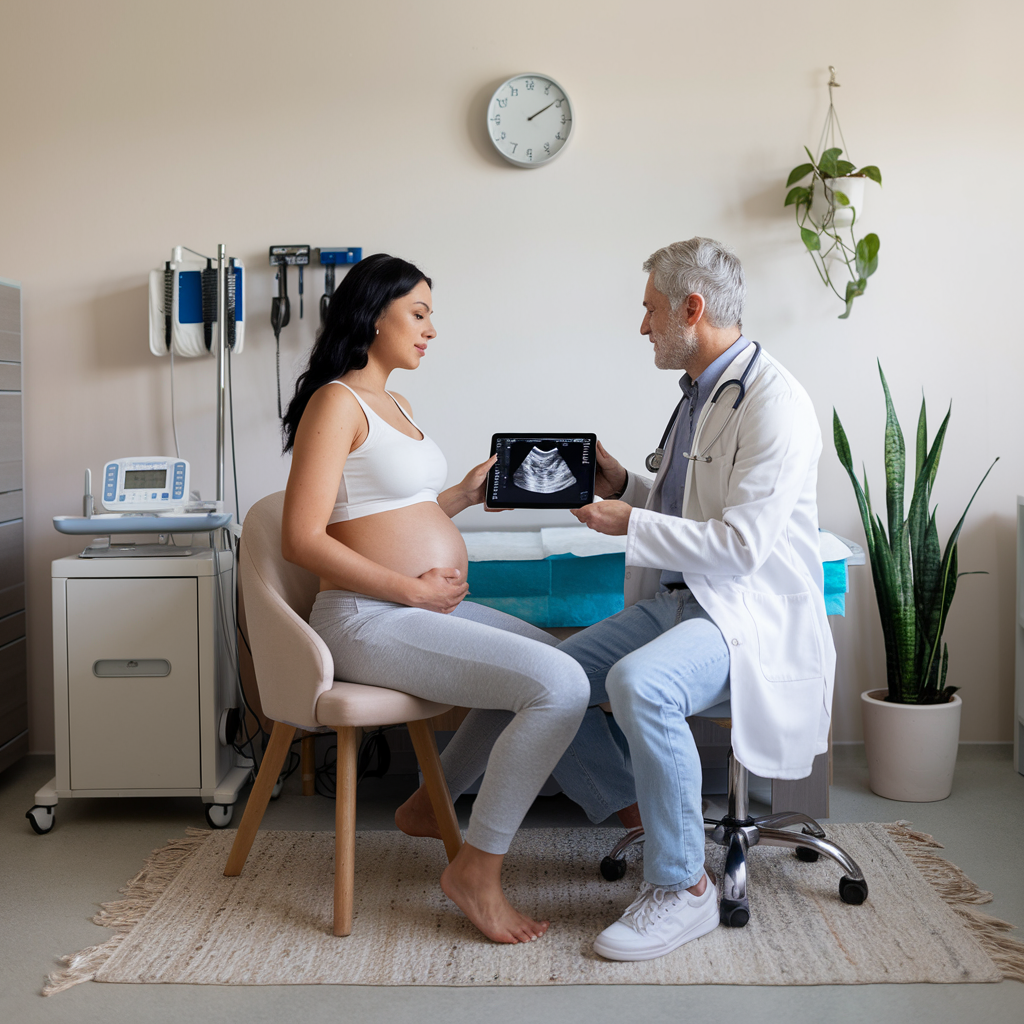
The Role of Ultrasounds in Prenatal Care
Ultrasounds are one of the most exciting aspects of pregnancy, as they allow parents to see their baby for the first time. But beyond providing a precious keepsake, ultrasounds play a critical role in assessing the health of the baby and the pregnancy.
1. Confirming Pregnancy and Determining Gestational Age
The first ultrasound, usually performed between 6 to 9 weeks, confirms the pregnancy and determines the gestational age of the baby. This is crucial for ensuring the pregnancy is progressing on the expected timeline. Early ultrasounds also help rule out any early complications such as ectopic pregnancies.
2. Monitoring Baby’s Growth
A more detailed ultrasound, known as the anatomy scan, is usually performed between 18 to 22 weeks. During this scan, the sonographer examines the baby’s organs, limbs, spine, and brain to ensure everything is developing correctly. This ultrasound can also reveal the baby’s gender, although not all parents choose to find out.
The anatomy scan is critical for identifying potential structural abnormalities in the baby. If an issue is detected, further tests and consultations with specialists may be required to create a plan for the rest of the pregnancy and delivery.
3. Assessing Placenta and Amniotic Fluid Levels
Ultrasounds also help assess the condition of the placenta, which provides oxygen and nutrients to the baby. If the placenta is not functioning correctly, the baby’s growth could be affected, and medical intervention may be necessary.
Amniotic fluid levels are another key aspect of the ultrasound. Too much or too little fluid can indicate potential issues such as gestational diabetes or kidney problems in the baby. Regular ultrasounds help keep track of these levels and guide any needed interventions.
4. Ensuring Proper Fetal Position
As the due date approaches, an ultrasound may be used to check the baby’s position. If the baby is in a breech position (feet or buttocks first), your healthcare provider can discuss options for delivery or ways to help the baby move into the correct position.
The Importance of Screenings in Prenatal Care
Screenings during pregnancy are essential for identifying any potential genetic or chromosomal conditions in the baby. These screenings provide critical information that can help parents prepare for any challenges their baby might face.
1. Genetic Screening
During the first trimester, a blood test combined with an ultrasound can help screen for chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome or Trisomy 18. While these tests don’t provide a diagnosis, they can identify pregnancies at a higher risk for these conditions, prompting further testing if necessary.
2. Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
NIPT is a blood test performed as early as 10 weeks of pregnancy that screens for specific genetic conditions such as Down syndrome, Trisomy 13, and Trisomy 18. It is a highly accurate screening option and is particularly recommended for women who are over 35 or have a family history of genetic disorders.
3. Gestational Diabetes Screening
Around 24 to 28 weeks of pregnancy, most women undergo a glucose tolerance test to screen for gestational diabetes. This condition can lead to complications during delivery, so it’s essential to identify it early and manage it with a healthy diet and possibly medication.
Conclusion
Prenatal care is an indispensable part of a healthy pregnancy. Regular checkups, ultrasounds, and screenings provide the information and reassurance you need to navigate the journey toward parenthood. By monitoring both the baby’s growth and the mother’s health, these essential steps help ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy and delivery.
While every pregnancy is unique, prenatal care provides the medical oversight necessary to catch potential complications early, allowing for prompt treatment and the best possible outcome for both mother and baby. Whether it’s listening to your baby’s heartbeat, seeing them on an ultrasound, or getting crucial test results, prenatal care is your partner in welcoming your baby into the world.

